Amazing health benefits of Sweet Potato
Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas)
Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the bindweed or morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting, tuberous roots are a root vegetable.
It shows Anti-oxidant, hepatoprotective, antiinflammatory, antitumor, antidiabetic, antimicrobial, antiobesity, antiaging effects.
Click here for more information about the Anti-oxidant
Parts of plant used
Leaves, shoot and tuberous root
Vitamin and mineral content
Vitamin : A, C, E, B1, B2, B3, B6, B9
Minerals : Calcium, Iron, Magnesium, Manganese, Phosphorus, Potassium, Sodium, Zinc
Phenolic acids : Chlorogenic, Isochlorogenic, Caffeic, Cinammic, and Hydroxycinammic acids.
- Phenolic acids have been associated with color, sensory qualities, nutritional value as well as antioxidant properties of foods. They are more abundant in purple fleshed sweet potato than in the other colors varieties
• Protein contents of sweet potato leaves and roots range from 4.0% to 27.0% and 1.0% to 9.0%, respectively. The sweet potato could be considered as an excellent novel source of natural health-promoting compounds, such as beta-carotene and anthocyanins, for the functional food market.
• The major phytochemicals that are generally present in sweet potato are flavonoids, terpenoids, tannins, saponins, glycosides, alkaloids, steroids and phenolic acids. These constituents may vary with varieties depending on flesh and skin colours.
• varieties depending on flesh and skin colours. Orange varieties are particularly rich in beta-carotene, while purple sweet potato contains higher anthocyanin content than other varieties of sweet potato.
• Orange varieties are particularly rich in beta-carotene, while purple sweet potato contains higher anthocyanin content than other varieties of sweet potato
- Beta carotene is a terpenoid with a strongly colored red-orange pigment abundant in plants and fruits.
- Anthocyanins are members of the flavonoid group of phytochemicals responsible for the red, purple and blue pigments in many fruit and vegetables.
• The antioxidant activities of sweet potato have mostly been attributed to their anthocyanin and beta-carotene contents.
• peonidin and cyanidin(examples of anthocyanins) were only detected in purple fleshed sweet potato, not white and orange varieties. Luteolin (flavonoid) was found in orange and purple varieties but absent in the white ones
> Always prefer purple sweet potato.
Application, uses and benefits
1) The fiber and antioxidants in sweet potatoes promote gut health.
- The fiber content in sweet potatoes can help prevent constipation and promote regularity for a healthy digestive tract. Whereas Anti-oxidant content in sweet potato promote growth of good bacteria in guy and reduces the of free radical.
2) Maintains or improve eye health : It is good source of provitamin A in the form of beta-carotene. Whereas Vitamin A is important for improving eye health and good source of Anti-oxidant.
- Beta-carotene(provitamin A) is converted to vitamin A in your body which is used to form light-detecting receptors inside eyes.
3) Eating raw or boiled sweet potato improve eye health and boosts immunity.
4) Anthocyanins in purple sweet potatoes can protect the brain by reducing inflammation and preventing free radical damage.
- The potential of purple sweet potato extract to inhibit inflammatory brain diseases by suppressing lipopolysacharide (LPS) induced inflammatory responses have been demonstrated by a number of studies.
5) Young leaves are widely consumed as vegetable.
6) Sweet potato helps in controlling wrinkles and increases moisture content in the skin.
7) Sweet potato helps in quick healing of the wound, decreases swelling.
8) High concentration of anthocyanin and β‐carotene in sweet potato, combined with the high stability of the color extract make it a promising and healthier alternative to synthetic coloring agents in food systems.
9) Sweet potatoes are an important source of magnesium, whose deficiency has been reported to be linked with a higher risk of depression, stress and anxiety. Thus, sweet potatoes can replenish the body’s magnesium levels and help alleviate the symptoms of depression and anxiety-related behaviors in individuals.
10) The fibers, anthocyanin, polyphenols, and high radical scavenging activity contained in sweet potatoes are all important in the fight against cardiovascular diseases and free radical damage.
11) Sweet potatoes contain high levels of Vitamin A, C, E, Anti-oxidants and minerals all of which are useful in the promotion of proper skin and hair health.
12) Eating sweet potato regularly enhance memory, immunity, skin and hair health digestion and many more.
Formats of intake of sweet potato
1) Eat raw (but chew it properly)
2) Boiled : First boil sweet potato then mesh it and add jaggery/honey according to requirement and eat. - You should take this with milk also
• Boiling sweet potatoes retains more beta-carotene and makes the nutrient more absorbable than other cooking methods such as baking or frying. Up to 92% of the nutrient can be retained by limiting the cook time, such as boiling in a pot with a tightly covered lid for 20 minutes. Cooking with the skin on further helps to minimize leaching of nutrients including beta-carotene and vitamin C.
3) Chips/Fries
4) Roti/Chapati : fresh sweet potato is chipped, dried and then ground into flour; this is then mixed with wheat flour and baked into chapattis OR mesh boiled sweet potato in jowar flour, add ginger, garlic, green chilli paste and baked it into Chapati.
5) soup : boil sweet potato with rock salt and garlic, Ginger.
6) roasted
7) pickles
8) sweet potato halwa
- https://cookpad.com/in/recipes/6855907-sweet-potato-with-jaggerysweet-potato-halwa
Follow us
1) Instagram
2) Facebook
3) Pinterest
🙏🙏Subscribe and share for latest updates 🙏🙏
Refrence :
1) Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research December 2016; 15 (12): 2751-2761 ISSN: 1596-5996 (print)
2) sciencedirect.com
3) PUBMED
4) Breeding sciences : Breed Sci. 2017 Jan; 67(1): 52–61. ; PMCID: PMC5407917
5) Food Sci Nutr. 2019 Jun; 7(6): 1920–1945. ; PMCID: PMC6593376
6) https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/food-features/sweet-potatoes/
Subscribe for latest updates and share
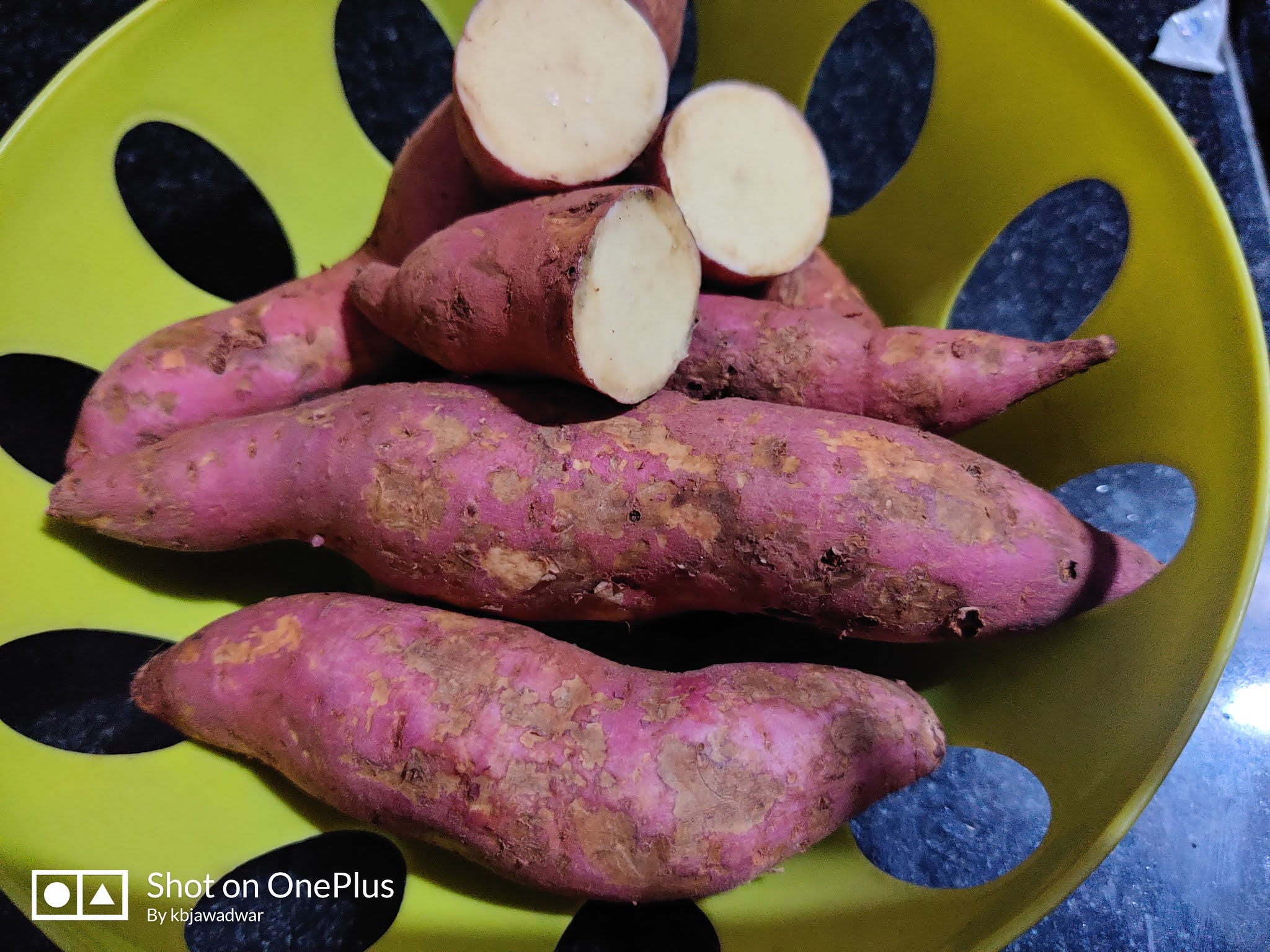





Very good information
ReplyDeleteNicely explained 👌
ReplyDeletetoptenclinic
ReplyDelete.